
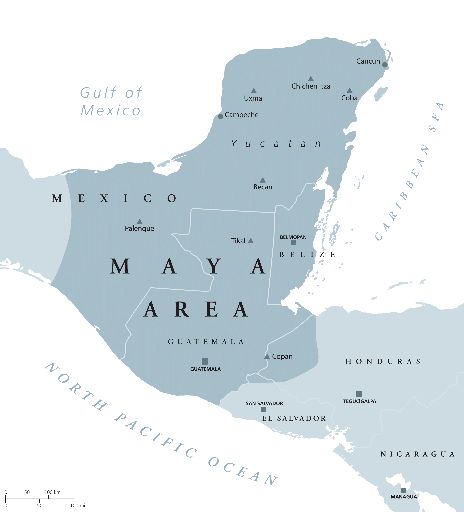

The Cochuah region on the Yucatán Peninsula thrived during the Terminal Classic after much of the south was depopulated due to drought and political conflict. However, a "collapse" in one area could be a time of "boom" in another.
"Less rainfall likely impacted canoe trade since water levels noticeably drop each dry season - so less rain meant less canoe travel," Lucero said. Lucero noted that some Maya areas experienced deforestation, and lower water levels made it harder to trade goods. The droughts, combined with political turmoil, would have also disrupted agriculture, maintenance of water storage systems and resulted in Maya rulers wasting resources on warfare, Shaw said. The problems the Maya suffered from droughts "caused people to lose trust in their rulers, which is more than just losing trust in the government when your rulers are closely tied to deities," said Justine Shaw, an anthropology professor at the College of the Redwoods in California. The fact that Maya rulers often linked their own powers to deities created more political problems. Related: Why does rain give off that fresh, earthy smell? "And since the most powerful Maya kings relied on urban reservoirs to draw in farmers/subjects during the annual dry season for access to clean drinking water, decreasing rainfall meant water levels dropped, crops failed and kings lost their means of power." What's more, "the decreasing rainfall exacerbated any problems kings were having," she said. Why did they fall?Ī mix of political and environmental problems is usually blamed for the decline of Maya cities.Īnalysis of speleothems, or rock structures in caves such as stalactites and stalagmites, shows that "several severe - multi-year - droughts struck between 800 and 930" in the southern Mesoamerica region, Lucero said. "We should always remember, the last Maya state, Nojpetén, fell only in 1697 - pretty recent," said Guy Middleton, a visiting fellow at the School of History, Classics and Archaeology at Newcastle University in the U.K. Maya states continued to exist even after the region was ravaged by war and disease brought about by the European conquests in Central America. While Mayapán declined prior to European contact, partly due to warfare, another Yucatán Peninsula site called Ti'ho was growing at the time Europeans arrived, Masson said. "Much of what we know about earlier Maya religion comes from books written in Mayapan's day and from descendant populations who met and survived European contact." "Mayapan had lords, priests, hundreds of religious hieroglyphic books, complex astronomy and a pantheon of deities," Masson said. When Chichén Itzá declined, largely because of a lengthy drought during the 11th century, another Yucatán Peninsula city, called Mayapán, started to thrive. "The Maya region was large, with many polities and environments, and multiple languages were spoken in the Maya family."

"Collapse is not a term that should be universally applied to 'the' Maya, who should not be referred to as a single term either," Marilyn Masson, a professor and chair of anthropology at the University at Albany, State University of New York, told Live Science in an email.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
